- EQUIPO MÉDICO PARA HOSPITALES
- Cardiología
- C.E.Y.E
- Instumental Medico
- Cuidados Intensivos
- Emergencias
- Ginecologia y Obstetricia
- Hospitalización
- Imagen
- Neonatología
- Quirófanos
- Recuperación
- Sillas y Bancos de Regadera
- Ventiladores de Terapia Intensiva
- EQUIPO MÉDICO PARA PACIENTES
- Accesorios para Baño
- Articulos Para Consultorio
- Auxiliares para Caminar
- Andadores
- Bastones
- Bastón con Asiento
- Bastón con Correa de Un Apoyo
- Bastón de 4 apoyos con base de plástico
- Bastón de Cuatro Apoyos con Base Ancha de Acero Cromado
- Bastón de Cuatro Apoyos con Base Angosta de Acero Cromado
- Bastón de Cuatro Apoyos con Base Angosta de Acero Cromado
- Bastón de Invidente Plegable
- Bastón de Madera
- Bastón de Madera Un Apoyo
- Muletas
- Bancos
- Básculas
- Accesorios
- Digitales
- Báscula Clínica Digital de baterías con Altímetro
- Báscula Digital Nivel de Ojo
- Báscula Digital para Silla de Ruedas Plegable
- Báscula digital pediátrica de baterias
- Báscula Digital Portátil
- Báscula Digital Uso Medico (Altura de la cintura)
- Báscula Pesa Bebés
- Báscula Pesa Bebés Digital
- Básculas Pesa Bebés Digital
- Manuales
- Báscula clínica mecánica con altímetro
- Báscula Mecánica Adulto
- Báscula Mecánica Adulto con Barra de Estatura
- Báscula Mecánica Con Barra de Estatura y Ruedas
- Báscula Mecánica Con Barra de Estatura y Ruedas
- Báscula Mecánica de Doble Lectura de Peso
- Báscula Mecánica de Doble Lectura de Peso y Barra de Estatura
- Báscula Mecánica de Doble Lectura de Peso, barra de estatura y soporte de manos
- Báscula Mecánica de doble lectura y ruedas
- Baumanómetro
- Biombo
- Buros
- Camas Tipo Hospital
- Carros De Emergencia
- Equipos de Rehabilitación
- Esterilizadores
- Estetoscopios
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Doble Adulto
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Doble Adulto "Acero Inoxidable"
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Doble Neonatal "Acero Inoxidable"
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Doble Pediátrico
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Doble Pediátrico "Acero Inoxidable"
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Sencilla Adulto
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Sencilla Pediátrico
- Estetoscopio de Pinard
- Estetoscopio Rappaport
- Gruas para paciente
- Lámparas Clinicas
- Línea Pediátrica
- Mesa de Exploracion
- Mesas
- Ortopedia Blanda
- Oximetros
- Porta Suero
- Recipientes de Acero Inoxidable
- Sillas de Ruedas
- Silla de Ruedas Cromada con Elevador de Pierna y Llanta Rellena
- Silla de Ruedas Cromada con Piesera Desmontable y Llanta Rellena
- Silla de Ruedas Cromada de Piesera y Brazo Fijo con Llanta Relle
- Silla de Ruedas Cromada Extra Ancha
- Silla de Ruedas Esmaltada con Llanta Neumática
- Silla de Ruedas Esmaltada de Lujo con Asiento de Nylon y Llanta
- Silla de Ruedas Reclinable Cromada
- Silla de Transporte
- Silla de Transporte
- Sillones Clinicos
- Sistemas de calentamiento
- Sistemas de entrenamiento
- Unidad de Criocirugía
- Accesorios Criocirugía
- 90060 N2O Cilindro (sin relleno)
- 901061 Cilindro de CO2 (sin relleno)
- Accu-Shield Spray concentrados en un área limitada (6 conos variada)
- Cesta para Cilindros (20 lb)
- UltraFreeze nitrógeno líquido pulverizador (0,3 litros) con 5 aberturas
- UltraFreeze nitrógeno líquido pulverizador (0,5 litros) con 5 aberturas
- Puntas Criocirugía
- Bolsa de 100 protectores de plástico desechables
- Punta Criocirugía, Flat (T-1900)
- Punta Criocirugía Bevel (T-0524)
- Punta Criocirugía Microderm (T0219)
- Punta Criocirugía T-0219 Cono
- Punta Criocirugía, Bevel (T-0823)
- Punta Criocirugía, 11.7mm HPV Tip (T-1200)
- Punta Criocirugía, 13.5mm HPV Tip (T-1300)
- Punta Criocirugía, 15.0mm HPV Tip (T-1500)
- Accesorios Criocirugía
- Welch Allyn
- Accesorios
- 2.5V Otoscopio de diagnóstico con espéculos
- 7.2v batería recargable
- Accesorios Kleenspec Sigmoidoscopio desechables
- Audiometría AM383/TM286 latiguillos individuales
- Audiometría AM383/TM286 latiguillos individuales
- Audiómetro Manual AM232, para corriente alterna solamente
- AudioScope tres formas de grabación, Welch Allyn
- AudioSpec Speculum ® Pequeño
- AudioSpec Speculum ® Grande
- AudioSpec Speculum ® Mediano
- Accesorios
- EQUIPO MÉDICO PARA DOCTORES
- Accesorios para Baño
- Articulos Para Consultorio
- C.E.Y.E
- Cuidados Intensivos
- Auxiliares para Caminar
- Andadores
- Bastones
- Bastón con Asiento
- Bastón con Correa de Un Apoyo
- Bastón de 4 apoyos con base de plástico
- Bastón de Cuatro Apoyos con Base Ancha de Acero Cromado
- Bastón de Cuatro Apoyos con Base Angosta de Acero Cromado
- Bastón de Cuatro Apoyos con Base Angosta de Acero Cromado
- Bastón de Invidente Plegable
- Bastón de Madera
- Bastón de Madera Un Apoyo
- Muletas
- Bancos
- Básculas
- Accesorios
- Digitales
- Manuales
- Báscula clínica mecánica con altímetro
- Báscula Mecánica Adulto
- Báscula Mecánica Adulto con Barra de Estatura
- Báscula Mecánica Con Barra de Estatura y Ruedas
- Báscula Mecánica Con Barra de Estatura y Ruedas
- Báscula Mecánica de Doble Lectura de Peso
- Báscula Mecánica de Doble Lectura de Peso y Barra de Estatura
- Báscula Mecánica de Doble Lectura de Peso, barra de estatura y soporte de manos
- Báscula Mecánica de doble lectura y ruedas
- Baumanómetro
- Biombo
- Buros
- Camas Tipo Hospital
- Carros De Emergencia
- Equipos de Rehabilitación
- Esterilizadores
- Estetoscopios
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Doble Adulto
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Doble Adulto "Acero Inoxidable"
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Doble Neonatal "Acero Inoxidable"
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Doble Pediátrico
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Doble Pediátrico "Acero Inoxidable"
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Sencilla Adulto
- Estetoscopio Cápsula Sencilla Pediátrico
- Estetoscopio de Pinard
- Estetoscopio Rappaport
- Gruas para paciente
- Lámparas Clinicas
- Línea Pediátrica
- Mesa de Exploracion
- Mesas
- Ortopedia Blanda
- Oximetros
- Porta Suero
- Recipientes de Acero Inoxidable
- Sillas de Ruedas
- Silla de Ruedas Cromada con Elevador de Pierna y Llanta Rellena
- Silla de Ruedas Cromada con Piesera Desmontable y Llanta Rellena
- Silla de Ruedas Cromada de Piesera y Brazo Fijo con Llanta Relle
- Silla de Ruedas Cromada Extra Ancha
- Silla de Ruedas Esmaltada con Llanta Neumática
- Silla de Ruedas Esmaltada de Lujo con Asiento de Nylon y Llanta
- Silla de Ruedas Reclinable Cromada
- Silla de Transporte
- Silla de Transporte
- Sillones Clinicos
- Sistemas de calentamiento
- Sistemas de entrenamiento
- Unidad de Criocirugía
- Accesorios Criocirugía
- 90060 N2O Cilindro (sin relleno)
- 901061 Cilindro de CO2 (sin relleno)
- Accu-Shield Spray concentrados en un área limitada (6 conos variada)
- Cesta para Cilindros (20 lb)
- UltraFreeze nitrógeno líquido pulverizador (0,3 litros) con 5 aberturas
- UltraFreeze nitrógeno líquido pulverizador (0,5 litros) con 5 aberturas
- Puntas Criocirugía
- Bolsa de 100 protectores de plástico desechables
- Punta Criocirugía, Flat (T-1900)
- Punta Criocirugía Bevel (T-0524)
- Punta Criocirugía Microderm (T0219)
- Punta Criocirugía T-0219 Cono
- Punta Criocirugía, Bevel (T-0823)
- Punta Criocirugía, 11.7mm HPV Tip (T-1200)
- Punta Criocirugía, 13.5mm HPV Tip (T-1300)
- Punta Criocirugía, 15.0mm HPV Tip (T-1500)
- Accesorios Criocirugía
- Welch Allyn
- Accesorios
- 2.5V Otoscopio de diagnóstico con espéculos
- 7.2v batería recargable
- Accesorios Kleenspec Sigmoidoscopio desechables
- Audiometría AM383/TM286 latiguillos individuales
- Audiometría AM383/TM286 latiguillos individuales
- Audiómetro Manual AM232, para corriente alterna solamente
- AudioScope tres formas de grabación, Welch Allyn
- AudioSpec Speculum ® Pequeño
- AudioSpec Speculum ® Grande
- AudioSpec Speculum ® Mediano
- Accesorios
- EQUIPO MÉDICO RENOVADO
- EQUIPO MEDICO NUEVO Y REACONDICIONADO DISTRIBUIDOR EXCLUSIVO
- Equipo Medico Nuevo y Reacondicionado
- Ambus
- Aspiradores de Secreción, Flemas y Accesorios
- Bases de Trapecio
- Doopler Dopplex
- Body Armor
- Espirómetros
- Estuches de Diagnostico
- Estuches de Disección
- Baterías
- Baumanometros y Brazaletes
- Sondas
- Bolsas de Agua Hielo, Para Cama, Pierna y Orina
- Nebulizadores
- Brazos Auxiliares Para Sanitarios
- Camillas
- Mangueras
- Férulas Neumáticas
- Trapecios
- Sillas y Bancos de Regadera
- Mesas y Charolas Para Paciente
- Bastones
- Micronebulizadores
- Perrillas
- Plicometros
- Purificadores
- Manómetros
- Aerochambers
- Basculas Digitales, Electrónicas y Mecánicas
- Batas Médicas, Para Pacientes y Artículos Para Cirugía
- Videles
- Almohadas
- Refracciones para Equipo Médico
- Carros Rojos Para Emergencias
- Estetoscopios y Accessorios
- Glucómetros y Accesorios
- Guantes de Látex
- Instrumental Médico y Quirúrgico
- Mascarillas Para Oxígeno
- Muletas y Accesorios
- Termómetros
- Sillones
- Negatoscopios y Otoscopios
- Oxígeno - Productos Respiratorios
- Pistolas Infrarojo
- Seguridad de Baño Para Paciente
- Sillas de Ruedas y Accesorios
- PRODUCTOS POPULARES
- Urinales
- Riñones Sanitarios
- Camas y Accesorios
- Tens Electroestimulador y Accesorios
- Andadores y Accessorios
- Maletines
- Humidificadores
- Cojines
- Cánulas
- Agarraderas
- EQUIPO MEDICO VENTA Y RENTA SERVICIO A DOMICILIO DISTRIBUIDOR EXCLUSIVO
- Tracciones Cervical y de Cama
- Tablas de Masaje Plegable
- Aspiradores de Secreción, Flemas y Accesorios
- Carreolas Equipadas
- Apnea de Sueño
- Masajeador Facial
- Porta Sueros
- Espirómetros
- Oxígeno de Tanque y Accesorios
- Termómetros
- Sondas
- Nebulizadores
- Masajeadores
- Mangueras
- Botiquines
- Bastones
- Aertovents
- Vaporizadores
- Aerochambers
- OFERTA DEL MES


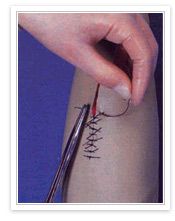
Inicio » Productos » EQUIPO MÉDICO PARA HOSPITALES » Instumental Medico » Surgical Suture
Instumental Medico
|
Suture material
These sutures can further be
Features
Nonabsorbable Sutures Features All nonabsorbable sutures are manufactured keeping in mind several fundamental characteristics, such as follows:
|

Los más recientes
- Aviso de Privacidad 2013.05.27 Aviso de Privacidad
- Agarraderas 2011.03.04 Agarraderas
- Bastones 2011.03.04 Bastones
© Copyright 2025 Medical Art
Privacy Policy l Terms & Conditions.
Powered by Infinity Computers